BPMN process modelling: tools and best practices
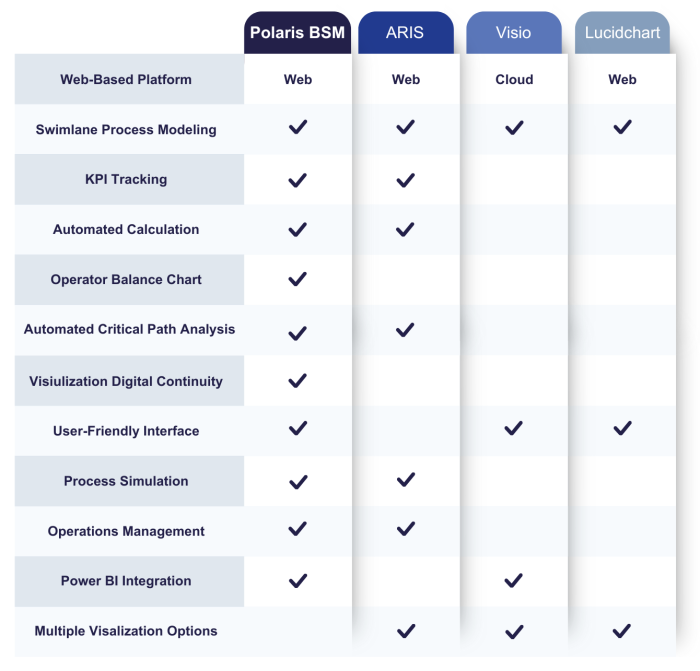
Comparison of different BPMN software
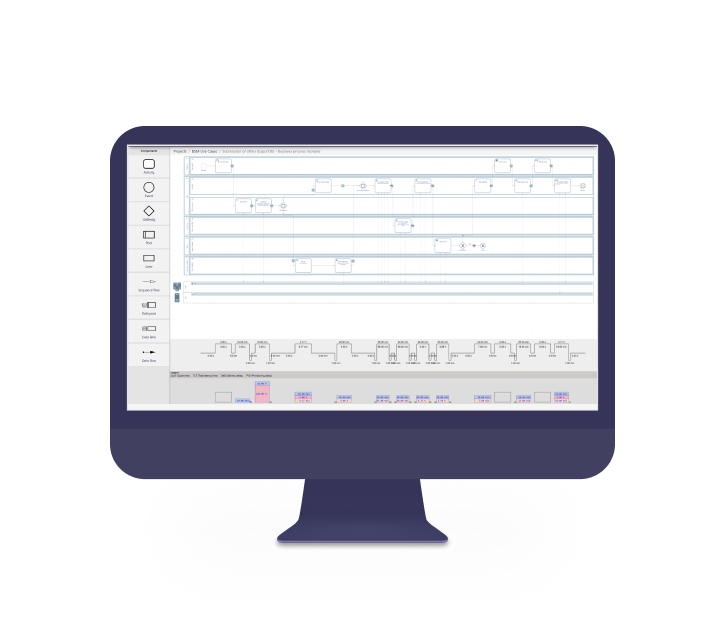
Polaris BSM
Polaris BSM is a web-based tool that has been specially developed for the comprehensive optimisation of business processes. It offers a wide range of functions that go beyond pure process modelling, such as KPI tracking, automated calculations and critical path analysis. Particularly noteworthy is the possibility of process simulation and the integration of Power BI, which enables in-depth analyses and visual evaluations. Thanks to a user-friendly interface, Polaris BSM is suitable for companies that want to manage their processes holistically and optimise them continuously.
Main benefit: Complete platform with comprehensive functions that go beyond the standard process model. In particular, the critical path analysis and integration with Power BI offer in-depth process analysis and optimisation.
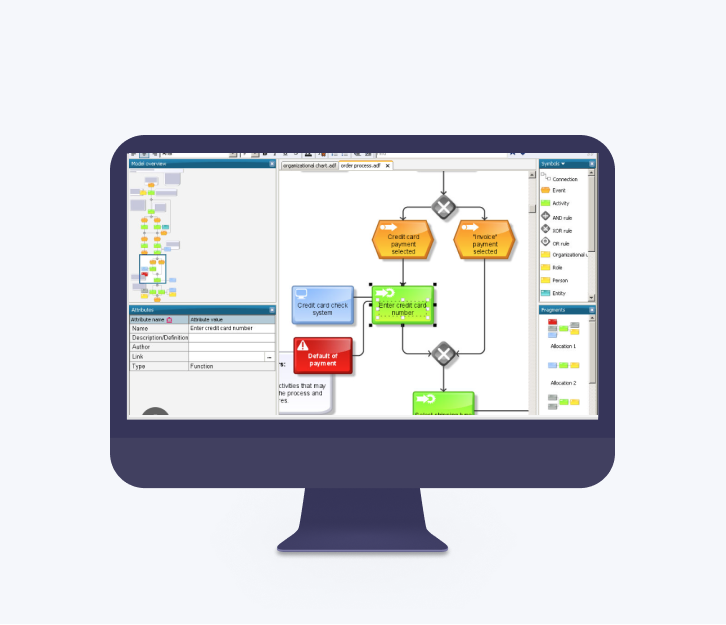
ARIS
ARIS is a well-known, web-based solution for process modelling that scores particularly well with its support for Swimlane process modelling and KPI tracking. It is ideal for companies that want to map and structure their business processes in detail. The option of critical path analysis is another plus point for identifying bottlenecks in the workflow.
Main benefit: Powerful tool for modelling and analysing complex business processes with a strong integration of Swimlane modelling.
Main disadvantage: ARIS is less user-friendly.
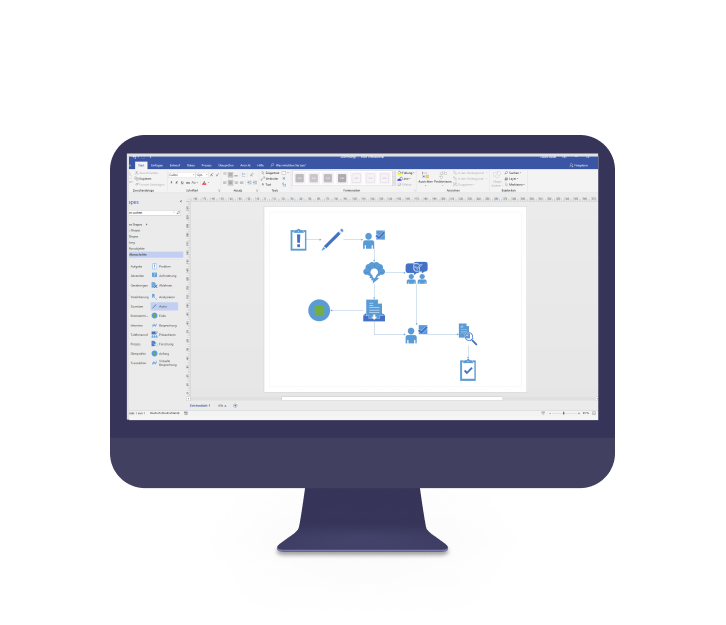
Visio
Visio from Microsoft is a cloud-based application that is particularly suitable for simple diagramming and visual modelling of processes. It is a good choice for teams who need to create superficial process diagrams quickly and easily. Visio also offers integration with Microsoft Power BI, which is useful for visualising processes with real-time data.
Main benefit: Simple and easy to use, especially integrated with Microsoft ecosystem.
Main disadvantage: Limited features in terms of process optimisation and simulation. Lacks advanced analytical functions such as critical path analysis.
Lucidchart
Lucidchart is a web-based tool that specialises in the visual representation of processes and diagrams. It is particularly suitable for people who need a simple user interface. Lucidchart also offers multiple visualisation options.
Main benefit: Easy to use and ideal for people who want to draw simple diagrams and process models.
Main disadvantage: Compared to Polaris or ARIS, it lacks advanced features such as critical path analysis or process simulation, which limits the depth of process optimisation.
Polaris BSM offers the most comprehensive solution for companies that want to optimise their processes and identify bottlenecks thanks to its extensive functions, particularly in the areas of KPI tracking, process simulation and critical path analysis. While other tools such as ARIS or Visio have their strengths, they are not as holistic and in-depth in their analysis and optimisation as Polaris.
Best Practices in Business Process Mapping and Notation
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a powerful tool for visualising and analysing business processes. It enables companies to precisely visualise and understand their process flows in order to identify bottlenecks, optimise inefficient processes and ensure continuous improvement. In this article, we will show you the best practices for efficiently designing and improving your process chains with the help of BPMN.
1. Process analysis through visualisation
Clear and comprehensive visualisation is the first step towards optimising processes. BPMN makes it possible to visualise complex process flows in a detailed and comprehensible way. By visualising all process steps, roles and decision points, it is possible to identify critical points where the workflow could come to a standstill.
Tip: Use BPMN to capture the entire process flow and thus visualise potential bottlenecks at an early stage.
2. Identifying bottlenecks
Bottlenecks often occur at points where resources are used inefficiently, unnecessary waiting times occur or the flow of information is disrupted. BPMN models help to identify these bottlenecks by visualising the entire process in individual steps and sequences. Critical process points can be identified and analysed, particularly through the use of time events and gateways.
Tip: Use time events and gateways to visualise delays or bottlenecks in decision-making processes.
3. Optimisation of decision-making processes with gateways
Gateways are a central element in BPMN for modelling decision processes and branches within a workflow. By using parallel, exclusive or event-based gateways correctly, you can check whether the decision-making process is running efficiently or whether bottlenecks occur at certain points. This makes it easier to identify and eliminate unnecessary loops or redundant decisions.
Tip: Use gateways specifically to analyse branches in the process and optimise decision paths.
4. Analysis of resource allocations
A clear allocation of resources is crucial for the efficiency of processes. Swimlanes can be used to clearly visualise responsibilities within a BPMN model. This provides a clear view of which departments, systems or people are responsible for which tasks. This visualisation makes it easy to identify overloads or inefficient use of resources.
Tip: Use swimlanes to precisely analyse task and resource assignments and find opportunities for improvement.
5. Use of sub-processes to reduce complexity
Large, complex processes are often difficult to analyse and optimise. Sub-processes help to reduce the complexity of a BPMN model by dividing larger processes into smaller, manageable units. This allows specific sub-processes to be analysed and improved in a targeted manner without having to change the entire model at once.
Tip: Use sub-processes to divide complex processes into manageable segments to enable detailed analysis and optimisation.
6. Continuous process improvement
BPMN models should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure that processes meet current requirements and circumstances. By constantly reviewing and analysing BPMN diagrams, inefficient processes can be quickly identified and adapted. This helps to avoid bottlenecks and improve the overall performance of the company.
Tip: Implement regular process reviews and use BPMN to continuously optimise your process chains.
7. Process simulation and scenario analysis
A major advantage of BPMN tools is the ability to carry out process simulations. This allows you to test ‘what-if’ scenarios and simulate the effects of changes to the process flow before they are actually implemented. This helps to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in advance and make well-founded decisions on process optimisation.
Tip: Use simulation tools to test alternative process flows and find the best solution to optimise resource utilisation and minimise lead times.
8. Improving communication and collaboration
A BPMN diagram is not only a tool for process management, but also an effective means of communication. It helps to get all stakeholders on the same page. By making BPMN diagrams clear and understandable, you facilitate collaboration between different departments and teams and create a common understanding of optimisation approaches.
Tip: Use BPMN as a basis for communication to make process changes transparent and understandable for everyone.